In today's digital landscape, where web applications serve millions of users simultaneously, ensuring high availability, scalability, and optimal performance is paramount. This is where load balancing comes into play, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a robust solution through its Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) service. In this guide, we'll dive deep into setting up an Application Load Balancer (ALB) with AWS EC2 instances, harnessing the power of cloud computing to achieve seamless and efficient workload distribution.
Understanding Load Balancing
Before delving into the setup process, let's grasp the concept of load balancing. Load balancing involves distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers, known as instances in AWS terminology. This distribution optimizes resource utilization, prevents overload on individual servers, and enhances overall application performance and reliability.
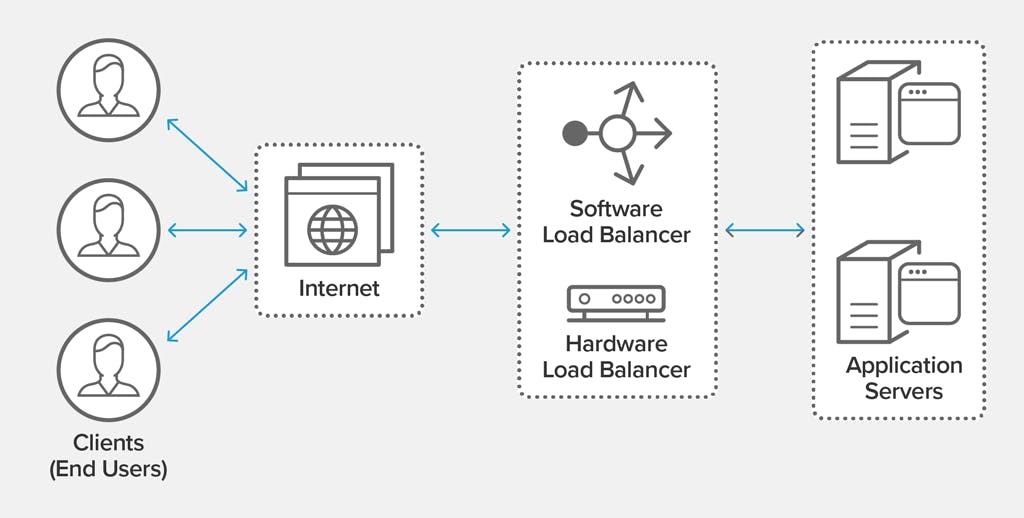
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) Overview
AWS ELB offers three types of load balancers tailored to different use cases:
Application Load Balancer (ALB): Operates at layer 7 of the OSI model, ideal for advanced routing and microservices.
Network Load Balancer (NLB): Operates at layer 4, suitable for high throughput and low latency applications.
Classic Load Balancer (CLB): Offers basic load balancing features at layer 4.
For this guide, we'll focus on setting up an Application Load Balancer (ALB) due to its flexibility and advanced capabilities.
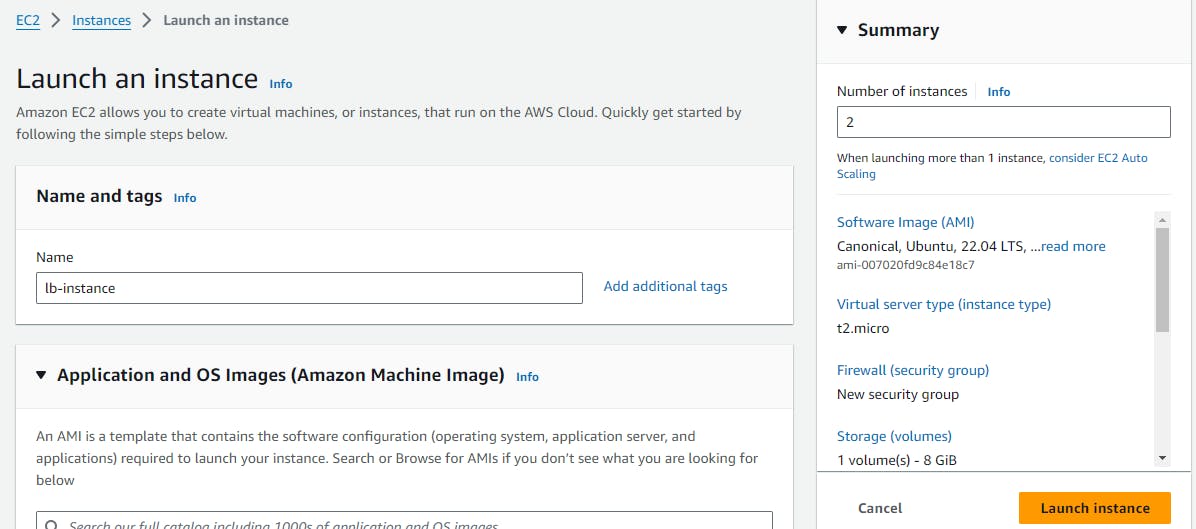
Task 1:
launch 2 EC2 instances with an Ubuntu AMI and use User Data to install the Apache Web Server.
Go to the EC2 dashboard after logging in to your Amazon Console.
Then, click the “Launch Instance” button write Name for instance choose “Ubuntu Server”.
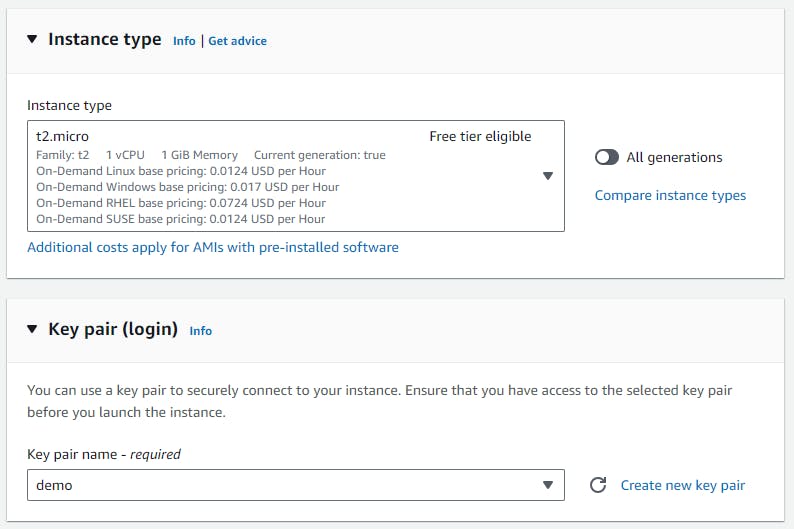
Choose an instance type “t2.micro”, Create new key pair or choose existing and set up the instance’s specifics.
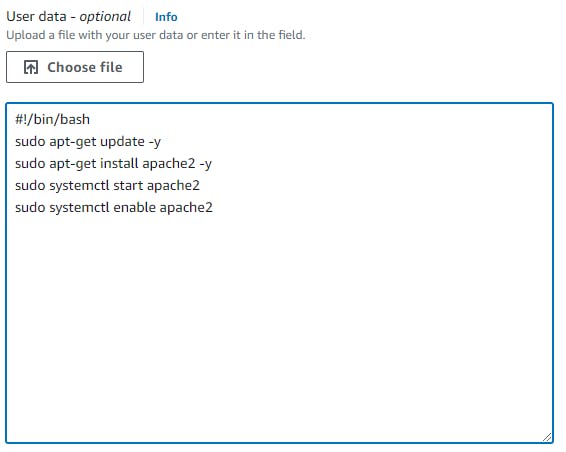
In the "Configure Instance Details" page, scroll down to the "Advanced Details" section and expand the "User data" field.
In the "User data" field, enter the following commands to install and start the Apache web server:
Two instances were created, as you can see.

Connect your ec2 instance.
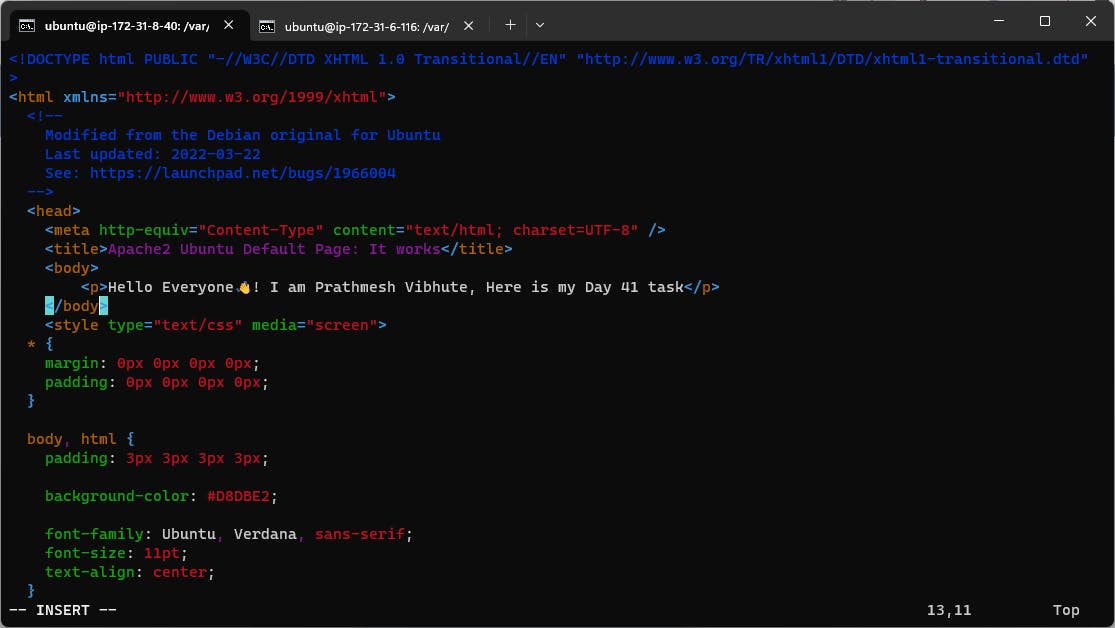
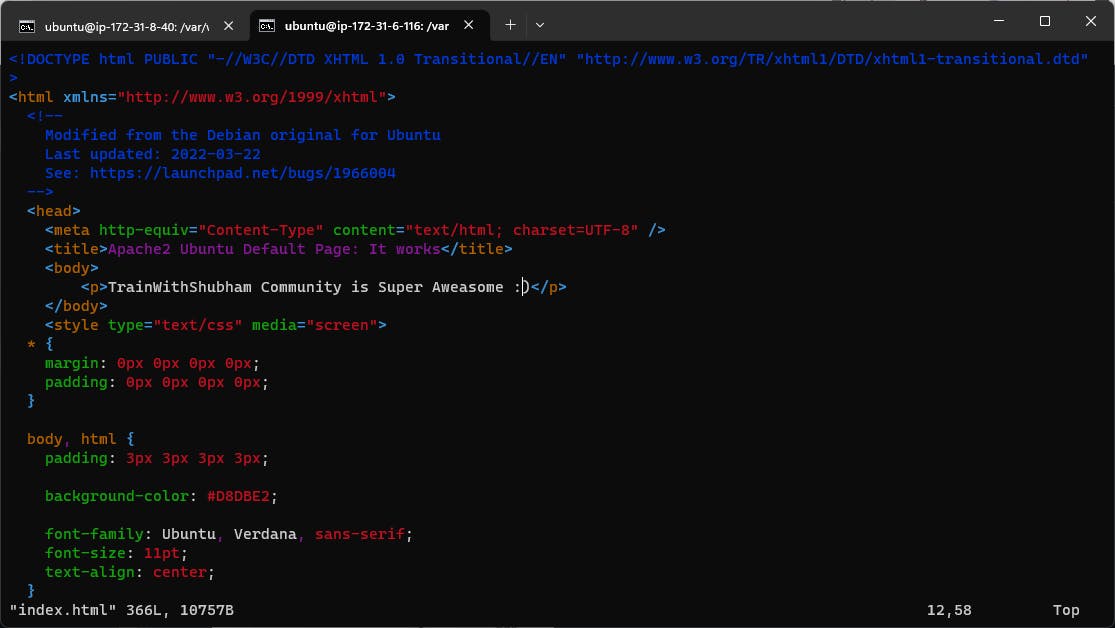
Modify the index.html file to include your name so that when your Apache server is hosted, it will display your name also do it for 2nd instance which include " TrainWithShubham Community is Super Aweasome :) ".
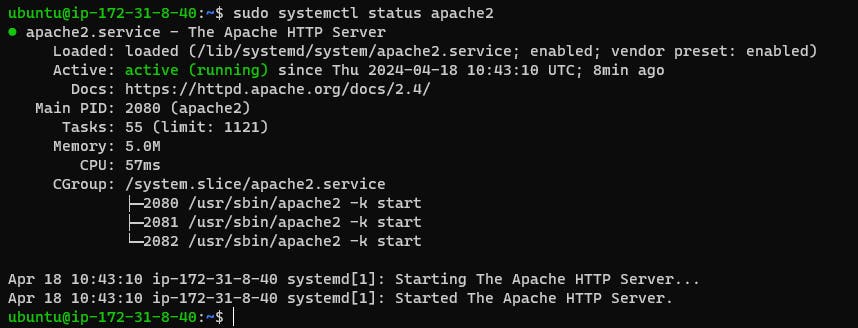
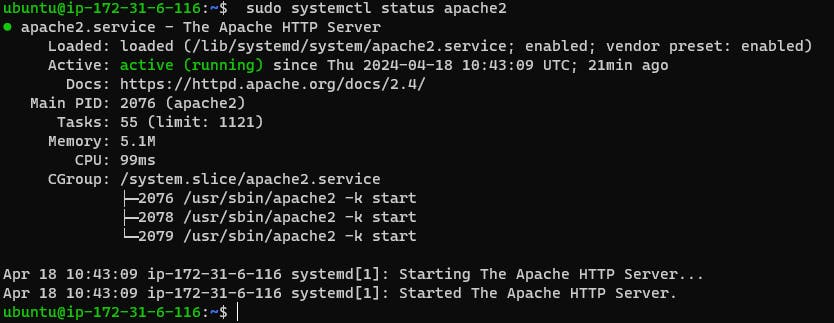
Use the command below to check the status of Apache 2:
sudo systemctl status apache2
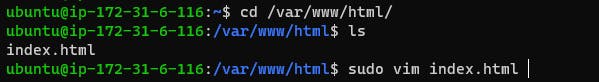
Go inside /var/www/html path and edit index.html file
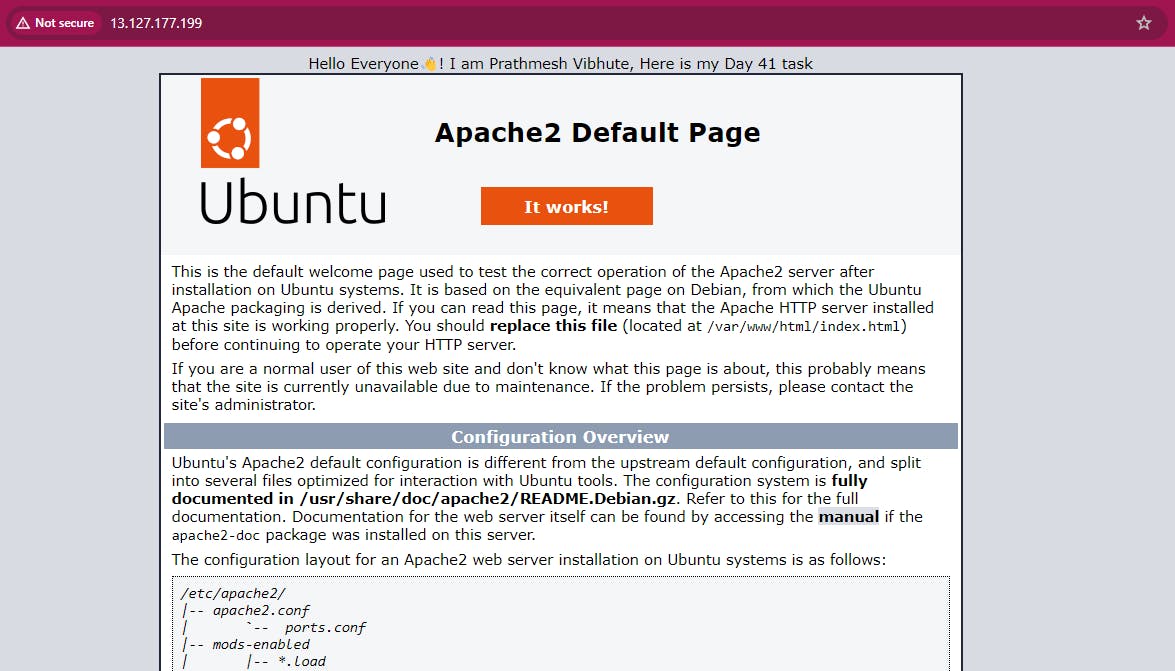
Copy the public IP address of your EC2 instances.
Open a web browser and paste the public IP address into the address bar.
You should see a webpage displaying information about your PHP installation.
For apache-server2:
Check apache2 status is active or not.
Go inside /var/www/html path and edit index.html file
Copy the public IP address of your EC2 instances.
Open a web browser and paste the public IP address into the address bar.
You should see a webpage displaying information about your PHP installation.

Task 2:
Create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) in EC2 using the AWS Management Console.
Log in to the AWS Management Console and go to the EC2 dashboard.
Click on "Load Balancers" in the left-hand navigation menu and then click the "Create Load Balancer" button.
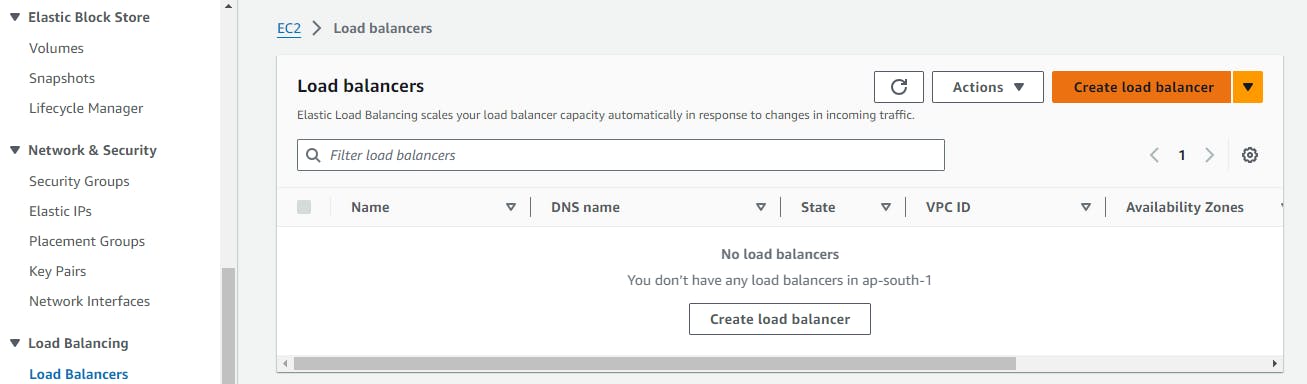
Select "Application Load Balancer" as the load balancer type and click "Create".
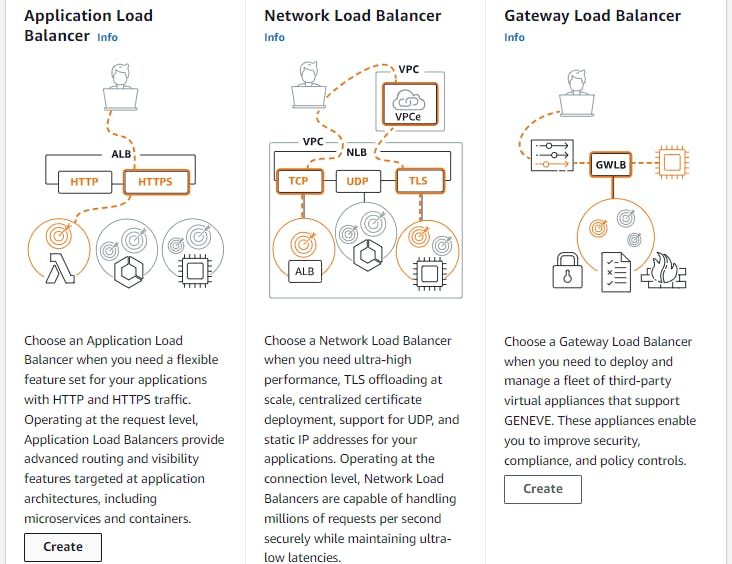
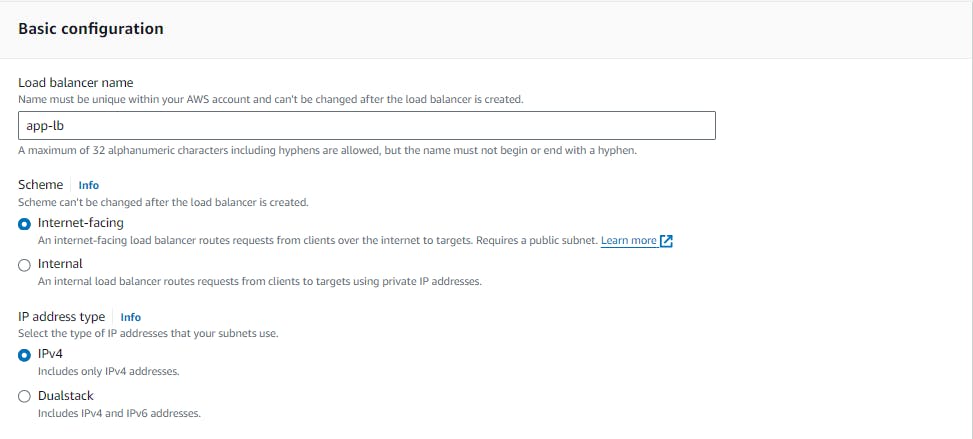
Configure the load balancer settings, such as name, listener, security group, and availability zones. For the listener, you can choose HTTP or HTTPS, depending on your application's requirements.
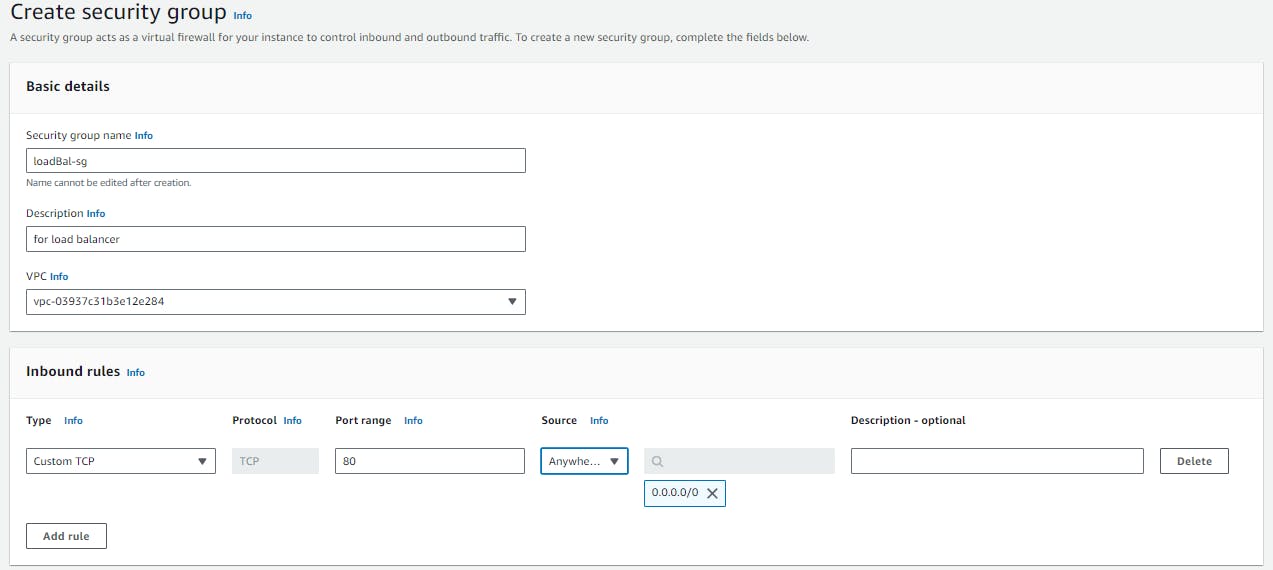
Configure "Security Groups" click on "create security group".
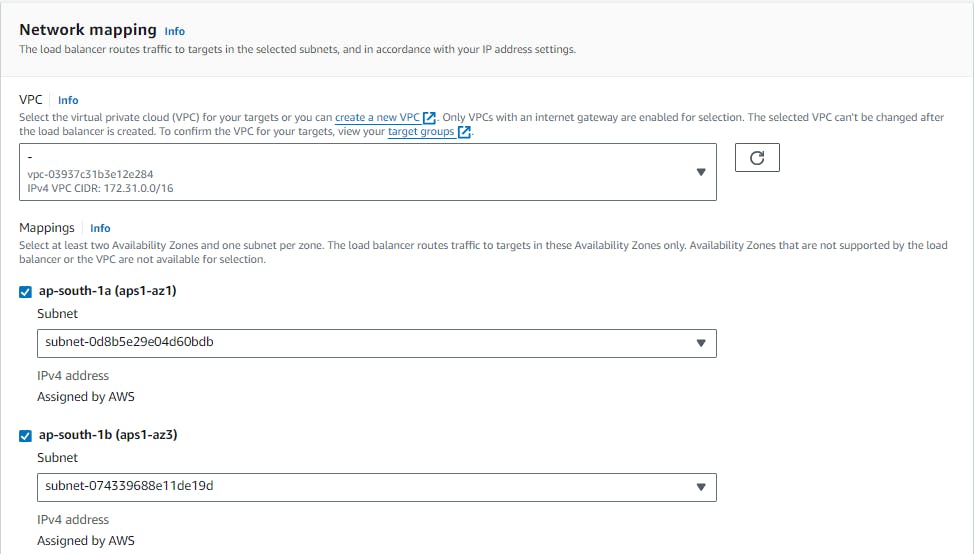
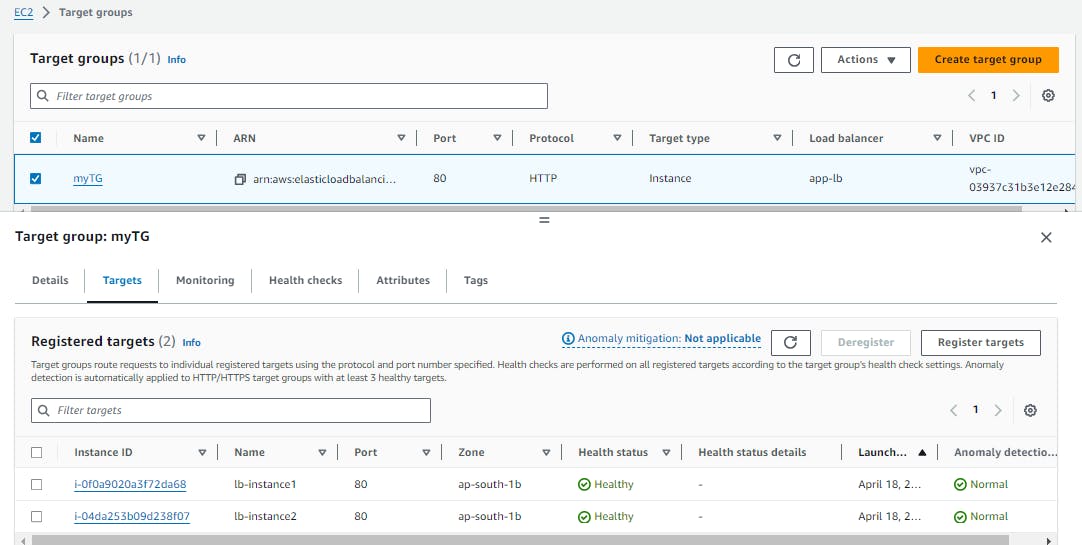
Create a target group by specifying a name, protocol, port, and health check settings. Choose the same availability zones as the load balancer and select the instances that you launched in Task 1 as targets for the target group.
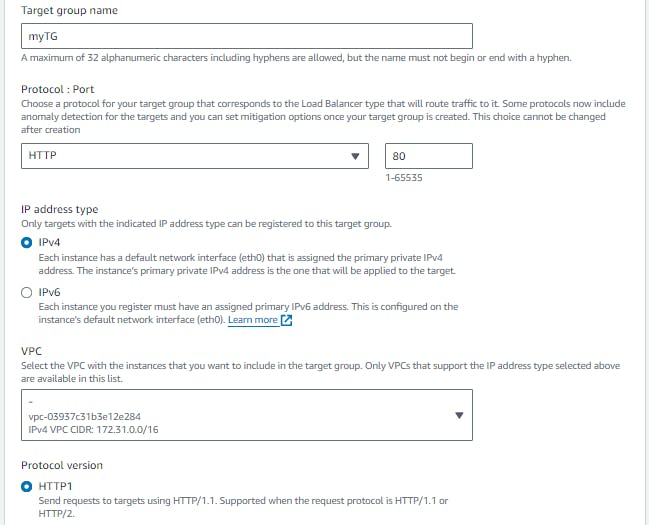
Add EC2 instances which you launch in task-1 to the ALB as target groups.
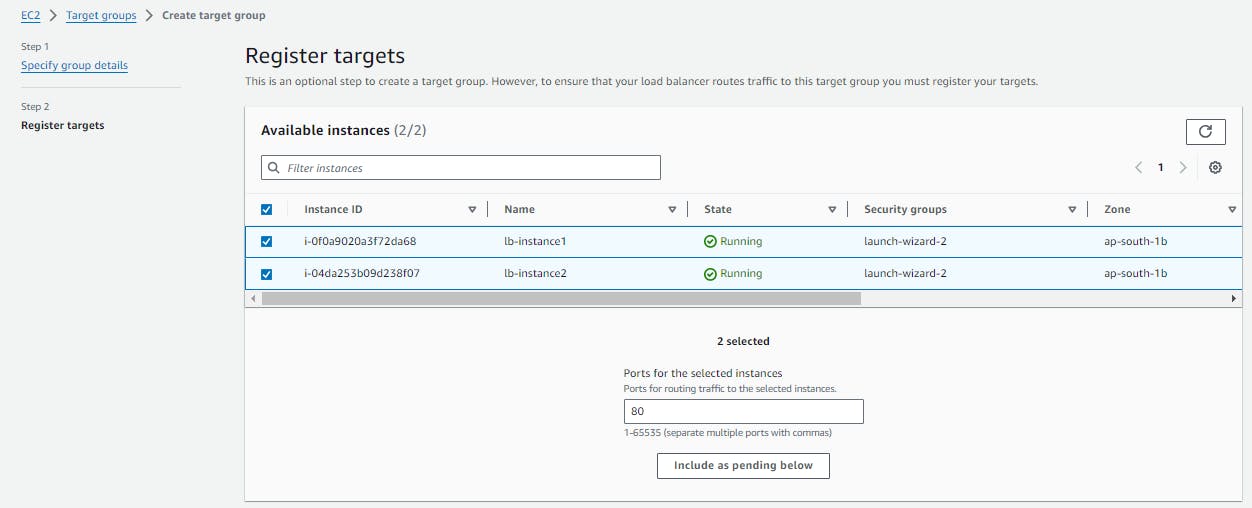
Target group is created.
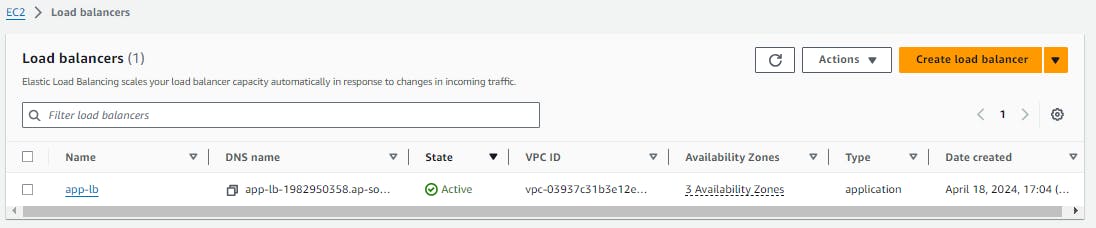
Load balancer is created.
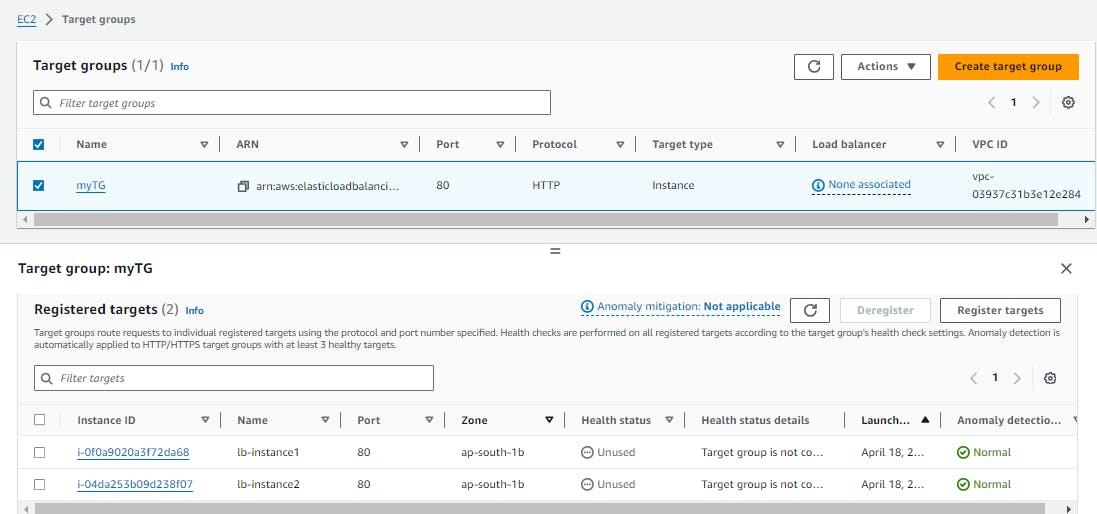
Verify that the ALB is working properly by checking the health status of the target instances and testing the load balancing capabilities.
Verify that the instances are registered with the load balancer by checking the target group's health status. You should see a healthy status for all instances in the group.
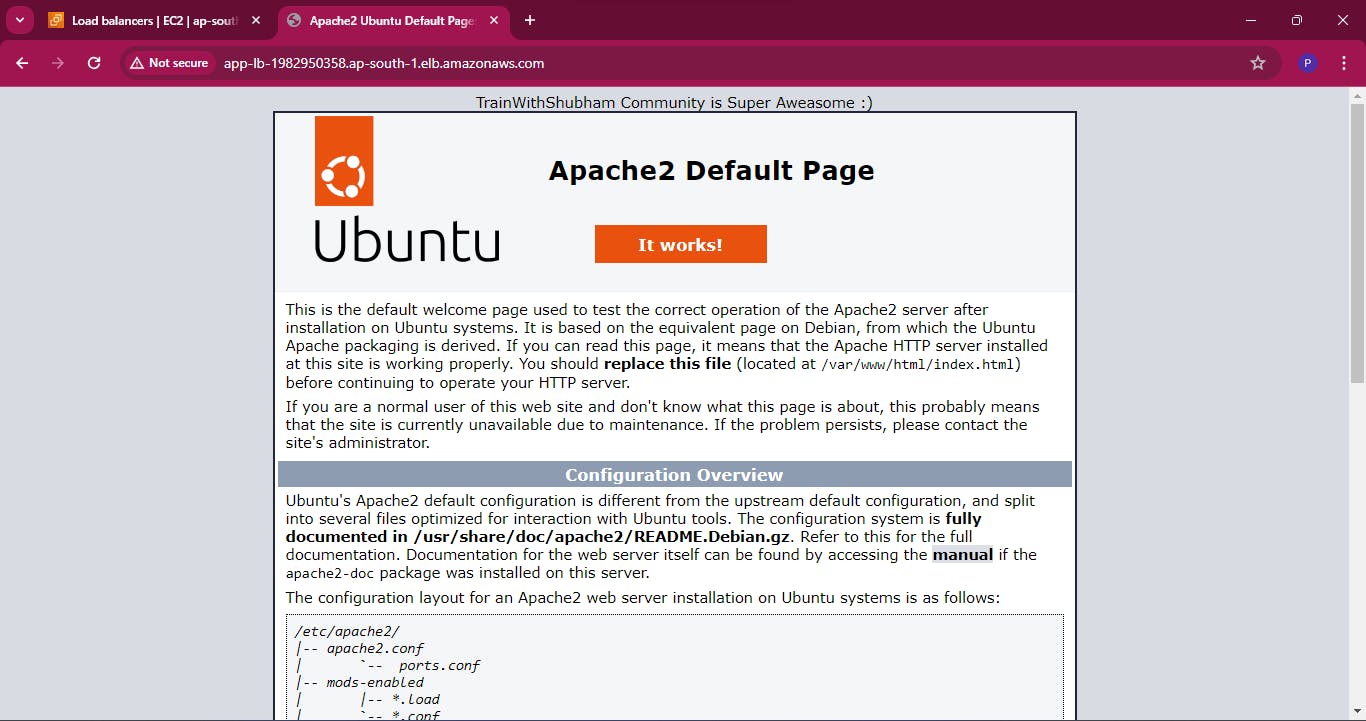
Test the load balancing capabilities by accessing the load balancer's DNS name in a web browser . You should see traffic being evenly distributed across the instances.
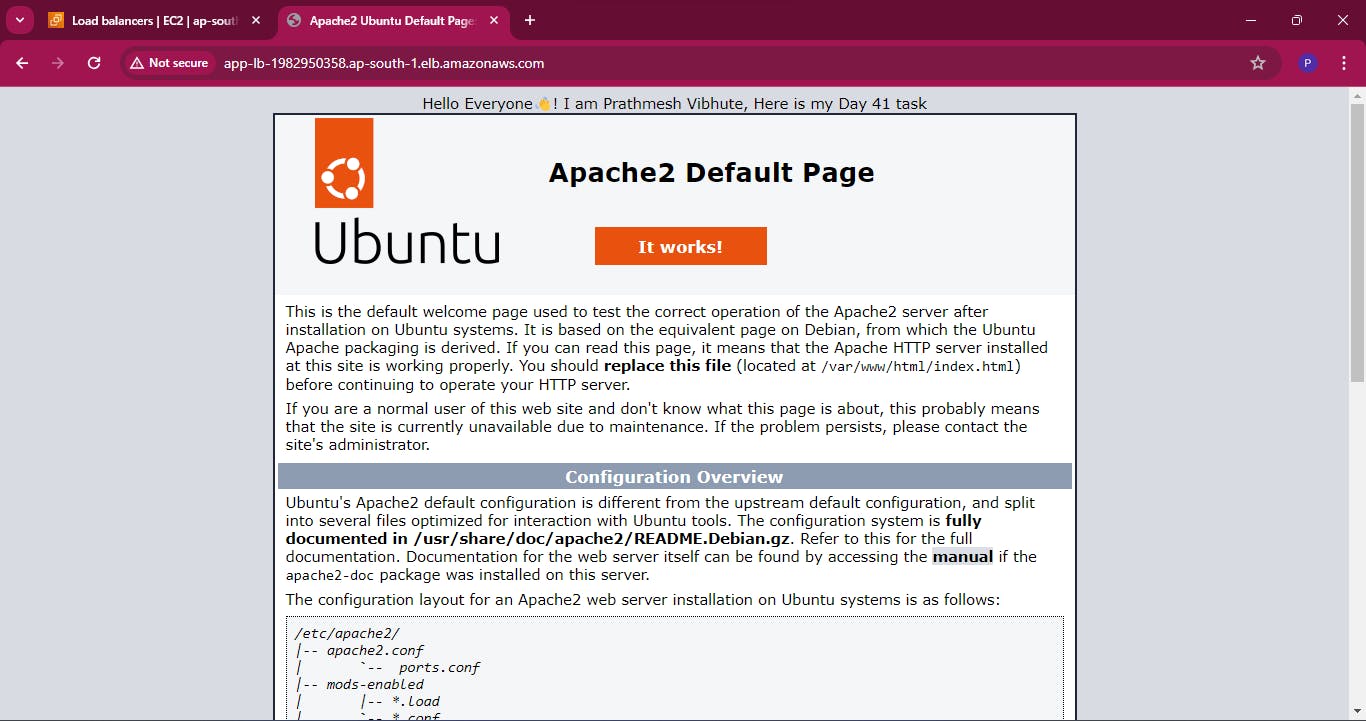
Conclusion
By following these steps, you've successfully set up an Application Load Balancer (ALB) with AWS EC2 instances, enhancing your application's scalability, reliability, and performance. Load balancing is a fundamental component of modern cloud architectures, and AWS ELB provides a robust platform to manage and optimize your workload distribution seamlessly in the cloud environment.
I'm confident that this article will prove to be valuable, helping you discover new insights and learn something enriching .
thank you : )
